利用弱监督学习在全切片病理图像中检测和分型基底细胞癌|文献速递-基于生成模型的数据增强与疾病监测应用
Title
题目
Detection and subtyping of basal cell carcinoma in whole-slide histopathology using weakly-supervised learning
利用弱监督学习在全切片病理图像中检测和分型基底细胞癌
01
文献速递介绍
基底细胞癌 (BCC) 的发病率正在给病理诊断带来压力。BCC 的发病率在所有肿瘤中最高,占美国、澳大利亚和欧洲所有皮肤癌病例的 70%以上。此外,BCC 的全球发病率正在迅速上升,有报告显示,在过去三十年中,发病率几乎翻了一倍(De Vries 等, 2005; Leiter 等, 2017; Lomas 等, 2012; Apalla 等, 2017)。
病理学家经常需要评估组织切片中是否存在 BCC 并提供其形态亚型信息。尽管目前没有正式的 BCC 分级系统,通常会根据特定的形态亚型将 BCC 区分为低风险和高风险(Kim 等, 2019)。虽然诊断 BCC 对于病理学家来说并不算困难,但需要评估的切片数量过多,尤其是在许多国家病理学家短缺的情况下,这种工作量可能是巨大的。
为了在未来使 BCC 诊断变得更加可控,人工智能 (AI) 算法在减少皮肤病理学家所需的时间和精力方面可以发挥重要作用。以往的研究中已使用深度学习,尤其是深度卷积神经网络 (CNN),用于 BCC 的检测。这些方法通常使用经验丰富的病理学家标注的像素级注释的小区域(Arevalo 等, 2015; Jiang 等, 2020)。然而,这种方法可能非常耗时且在 BCC 亚型分型上存在问题,因为高风险生长模式的精确标注更具挑战性。另一种替代方法是多实例学习 (MIL),该方法在处理大量皮肤活检并训练精确的 BCC 检测模型上效果显著,且不需要注释区域(Campanella 等, 2019)。但该方法假设良性切片中的所有区域均为良性,而标记为 BCC 的切片至少包含一个含有 BCC 的区域,这种假设会使网络局限于单个区域大小,从而导致数据利用效率较低。
聚类约束注意力多实例学习 (CLAM) 方法利用预训练的卷积神经网络将全切片图像编码为较小的特征集(每个区域一个特征向量)。然后,将聚合的特征向量通过一个注意力门、一个聚类头和一个分类头。此方法减少了网络视野的限制,且数据效率更高(Lu 等, 2021)。然而,该方法使用的是基于 ImageNet 预训练的固定编码器进行特征提取,可能会导致下游分类任务的特征次优,同时限制了输入图像的数据增强。
在本研究中,我们的目标是使用弱监督方法解决 BCC 及其亚型检测相关的挑战。我们的研究分为两个主要部分。第一部分聚焦于利用弱监督技术实现高准确度检测和分类结果的可行性,考虑到获取精确亚型信息和注释的实际影响和限制。
第二部分中,我们假设 Streaming CLAM 相较于 CLAM 能更有效地解决该问题。考虑 Streaming CLAM 模型的原因在于其能够利用 Pinckaers 等人(2019)提出的端到端 CNN 流式处理方法。该方法使得编码器可以学习 WSI 的任务特定特征表示(Pinckaers 等, 2022)并允许数据增强。我们假设这将带来更高的性能和更数据高效的弱监督学习方法,用于 BCC 的检测和分型。
1.1. 研究贡献
本研究在自动化 BCC 分类方面做出了几项重要贡献。首先,提出了一种基于弱监督学习的创新 BCC 检测和分型算法,结合流式和注意力机制,并与先进的基准进行对比。其次,本研究首次将该算法的分型性能与两位专家病理学家进行了对比,并在两个外部数据集上进行了进一步验证。第三,我们公开了最大规模的皮肤全切片图像数据集,涵盖含有和不含 BCC 的共计 5147 张图像,总计 666 GB。
Aastract
摘要
The frequency of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) cases is putting an increasing strain on dermatopathologists. BCCis the most common type of skin cancer, and its incidence is increasing rapidly worldwide. AI can play asignificant role in reducing the time and effort required for BCC diagnostics and thus improve the overallefficiency of the process. To train such an AI system in a fully-supervised fashion however, would require alarge amount of pixel-level annotation by already strained dermatopathologists. Therefore, in this study, ourprimary objective was to develop a weakly-supervised for the identification of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) andthe stratification of BCC into low-risk and high-risk categories within histopathology whole-slide images (WSI).We compared Clustering-constrained Attention Multiple instance learning (CLAM) with StreamingCLAM andhypothesized that the latter would be the superior approach. A total of 5147 images were used to train andvalidate the models, which were subsequently tested on an internal set of 949 images and an external setof 183 images. The labels for training were automatically extracted from free-text pathology reports usinga rule-based approach. All data has been made available through the COBRA dataset. The results showedthat both the CLAM and StreamingCLAM models achieved high performance for the detection of BCC, withan area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.994 and 0.997, respectively, on the internal test set and 0.983and 0.993 on the external dataset. Furthermore, the models performed well on risk stratification, with AUCvalues of 0.912 and 0.931, respectively, on the internal set, and 0.851 and 0.883 on the external set. In everysingle metric the StreamingCLAM model outperformed the CLAM model or is on par. The performance ofboth models was comparable to that of two pathologists who scored 240 BCC positive slides. Additionally, inthe public test set, StreamingCLAM demonstrated a comparable AUC of 0.958, markedly superior to CLAM’s0.803. This difference was statistically significant and emphasized the strength and better adaptability of theStreamingCLAM approach.
基底细胞癌 (BCC) 病例的频率正对皮肤病理学家造成日益增加的压力。BCC 是最常见的皮肤癌类型,且其发病率在全球范围内迅速上升。人工智能 (AI) 在减少 BCC 诊断所需的时间和精力方面可以发挥重要作用,从而提高整个过程的效率。然而,要以全监督的方式训练这样一个 AI 系统,则需要大量的像素级标注,这对已然负担过重的皮肤病理学家来说是极具挑战的。因此,本研究的主要目标是开发一种弱监督方法,以便在病理全切片图像 (WSI) 中识别基底细胞癌 (BCC) 并将其分为低风险和高风险类别。
我们比较了聚类约束的注意力多实例学习 (CLAM) 和 StreamingCLAM,假设后者是更优的方法。共有 5147 张图像用于模型的训练和验证,随后在内部测试集 (949 张图像) 和外部测试集 (183 张图像) 上进行了测试。训练标签通过基于规则的方法从病理报告的自由文本中自动提取。所有数据都通过 COBRA 数据集公开提供。结果显示,CLAM 和 StreamingCLAM 模型在检测 BCC 方面都表现出高性能,在内部测试集上分别达到了 0.994 和 0.997 的 ROC 曲线下面积 (AUC),在外部数据集上则分别达到了 0.983 和 0.993。此外,这些模型在风险分层方面的表现也很好,在内部数据集上的 AUC 值分别为 0.912 和 0.931,而在外部数据集上分别为 0.851 和 0.883。在每一个指标上,StreamingCLAM 模型均优于或与 CLAM 模型持平。两种模型的性能与两位对 240 张 BCC 阳性切片进行评分的病理学家相当。此外,在公开测试集上,StreamingCLAM 展现出 0.958 的 AUC,显著优于 CLAM 的 0.803。此差异在统计学上具有显著性,突显了 StreamingCLAM 方法的优势及其更强的适应性。
Method
方法
3.1. Tissue segmentation and packing
In the process of digitizing pathological biopsies, a significantamount of white space may be present due to the small size of thebiopsy resulting in cuts that take up little space on the glass slide. Toorganize the data more efficiently for training both weakly-supervisedtechniques, two pre-processing steps were implemented.The first step involved the detection of tissue within the biopsy samples. By identifying tissue regions, the white space can be eliminated orskipped. A fully-supervised, patch-based, DenseNet model was trainedon 50 annotated slides for this purpose (see Fig. 2A). To enhance theaccuracy of segmentation around edges, a higher sampling rate wasapplied to annotations located near the edges of tissue, as opposedto random sampling outside of tissue, which often results in emptypatches. Additionally, more sampling was done in areas containingartifacts such as scratches and stains outside of tissue regions.An additional second step was executed for StreamingCLAM tominimize the input image size in order to process the entire imagewith the network. To accomplish this, a packer algorithm was implemented to tightly pack sections of tissue. This was achieved by utilizingthe findContours function from the opencv-python (4.5) library todetect individual objects in the tissue segmentation mask, extracting thebounding boxes, and using the python library rectangle-packer (2.0.1)to efficiently fill the canvas and minimize white space (see Fig. 2B).
3.1. 组织分割和包装
在数字化病理活检的过程中,由于活检样本的尺寸较小,切片在玻片上占据的空间很少,因此常会出现大量的空白区域。为提高数据的训练效率,特别是在弱监督技术的应用中,我们实施了两步预处理过程。
第一步是检测活检样本中的组织区域。通过识别组织区域,可以消除或跳过空白区域。为此,训练了一个基于全监督的、以切片为单位的 DenseNet 模型,模型基于 50 张标注的切片进行训练(见图 2A)。为了提高边缘区域的分割准确性,在组织边缘附近应用了更高的采样率,而非在组织外的随机采样,这样可以避免空白区域。此外,还增加了在包含划痕和污渍等伪影的区域进行采样的频率,以提升模型对这些区域的识别能力。
第二步是为 StreamingCLAM 优化输入图像的尺寸,以便网络能够处理整个图像。为此,我们实施了一种打包算法,以紧凑地排列组织区域。具体方法是利用 opencv-python (4.5) 库中的 findContours 函数检测组织分割掩膜中的单个对象,提取边界框,并使用 python 库 rectangle-packer (2.0.1) 高效填充画布,以最大限度地减少空白区域(见图 2B)。
Results
结果
4.1. Model performance
We evaluated the performance of the two models designed for eachdistinct task. The first task is to differentiate between non-BCC andBCC cases, while the second task involved assessing the risk of BCCin low-risk and high-risk cases.For the first task, on the internal test set, the StreamingCLAMmodel yielded a mean AUC of 0.997 (95% CI 0.995–0.999), marginallyoutperforming the CLAM model which had an AUC of 0.994 (95%CI 0.990–0.997). Although this performance gap is minute, spanningonly thousandths, DeLong’s test confirmed the difference to be statistically significant (Z = −2.2555, 𝑝-value = 0.0241, 95% CI: −0.0070 to−0.0004). On the external test set, while the StreamingCLAM model’smean AUC of 0.993 (95% CI 0.986–1.000) showed a slightly largergap over the CLAM model’s mean AUC of 0.983 (95% CI 0.969–0.998)compared to the internal set, this difference did not reach statisticalsignificance (Z = −1.5534, 𝑝-value = 0.1203, 95% CI: −0.0220 to0.0025).
我们评估了两个模型在各自不同任务中的性能。第一个任务是区分非基底细胞癌 (non-BCC) 和基底细胞癌 (BCC) 病例,第二个任务是评估 BCC 的低风险和高风险。
对于第一个任务,在内部测试集中,StreamingCLAM 模型的平均 AUC 为 0.997(95% 置信区间 0.995–0.999),略微优于 CLAM 模型,其 AUC 为 0.994(95% 置信区间 0.990–0.997)。尽管这一性能差异仅为千分位,但 DeLong 检验确认了该差异在统计学上显著(Z = -2.2555,𝑝 值 = 0.0241,95% 置信区间:-0.0070 至 -0.0004)。在外部测试集中,StreamingCLAM 模型的平均 AUC 为 0.993(95% 置信区间 0.986–1.000),相较于 CLAM 模型的平均 AUC 0.983(95% 置信区间 0.969–0.998),差距稍大于内部测试集,但该差异未达到统计显著性(Z = -1.5534,𝑝 值 = 0.1203,95% 置信区间:-0.0220 至 0.0025)。
Figure
图
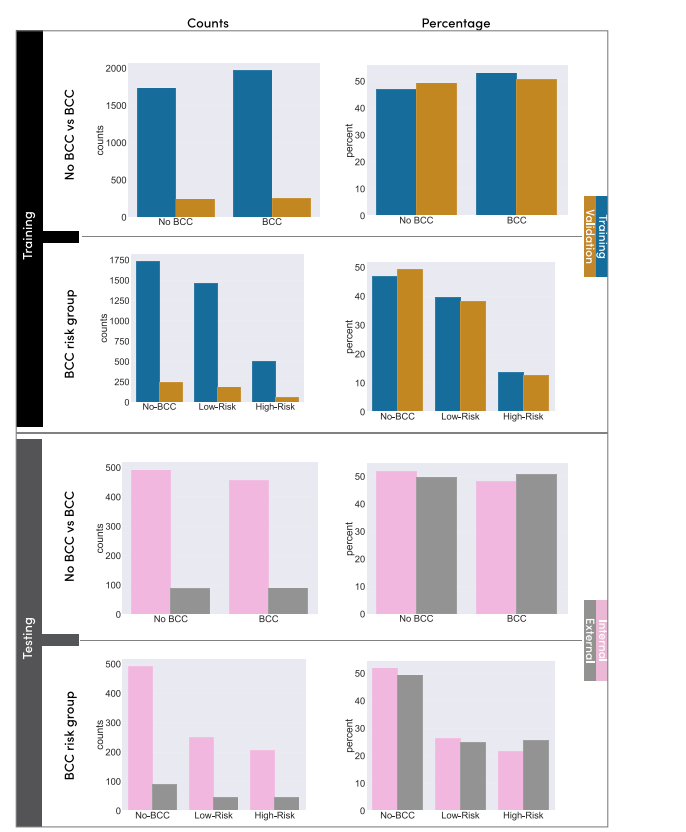
Fig. 1. Overview of the data and label distribution of the training and testing sets. The training set is divided into a training subset and a validation subset, while the testing setis divided into an internal and an external test set. The first column shows the absolute number of cases for each set, and the second column presents the ratio.
1. 训练集和测试集的数据和标签分布概览。训练集分为训练子集和验证子集,而测试集分为内部测试集和外部测试集。第一列显示每个数据集的绝对病例数,第二列显示相应的比例。
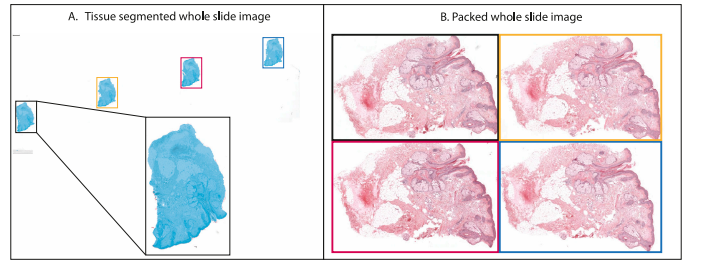
Fig. 2. Example of tissue segmentation and image packing. The left figure shows the output of the tissue segmentation model as a light-blue overlay on top of the originalwhole-slide image. The right figure shows the individual tissue pieces packed such as to minimize the white space between them.
图 2. 组织分割和图像打包示例。左图展示了组织分割模型的输出结果,作为浅蓝色叠加层覆盖在原始全切片图像上。右图展示了紧密排列的各个组织块,以最大程度减少它们之间的空白区域。
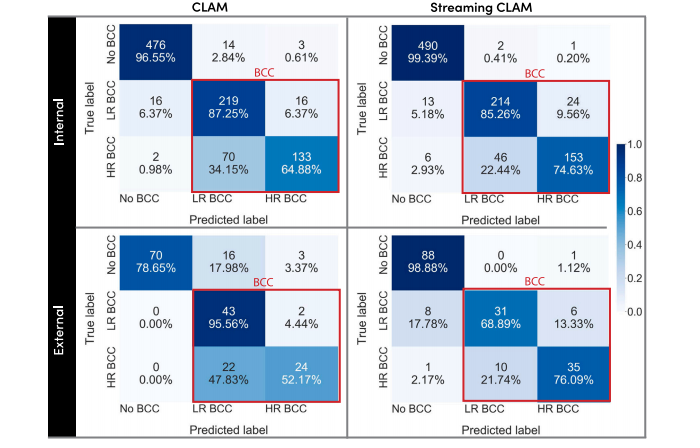
Fig. 3. Confusion matrices for both CLAM (left) and StreamingCLAM (right). The confusion matrices for both the internal and external test set are shown. The red box groups are true positive BCC.
图 3. CLAM(左)和 StreamingCLAM(右)的混淆矩阵。展示了内部和外部测试集的混淆矩阵。红色框内的部分表示基底细胞癌(BCC)的真正例数。
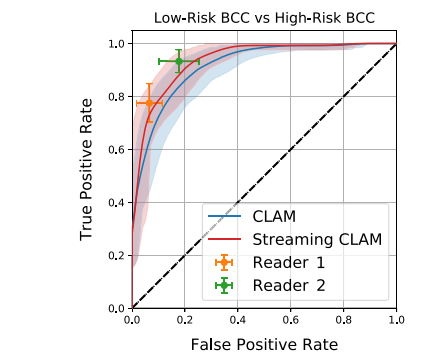
Fig. 4. Bootstrapped ROC Analysis for Discriminating Between Low-Risk and High-RiskBCC. The ROC curve displays the performance of two models in comparison to twopathologists in differentiating between low-risk and high-risk BCC. The curves of themodels are plotted with 95% CI and compared to the performance of the pathologists,also shown with 95% CI
4. 用于区分低风险和高风险基底细胞癌 (BCC) 的自助法 ROC 分析。ROC 曲线展示了两个模型在区分低风险和高风险 BCC 时的性能,并与两位病理学家的表现进行比较。模型的曲线绘制了 95% 置信区间,与病理学家的表现(同样带有 95% 置信区间)进行了对比。
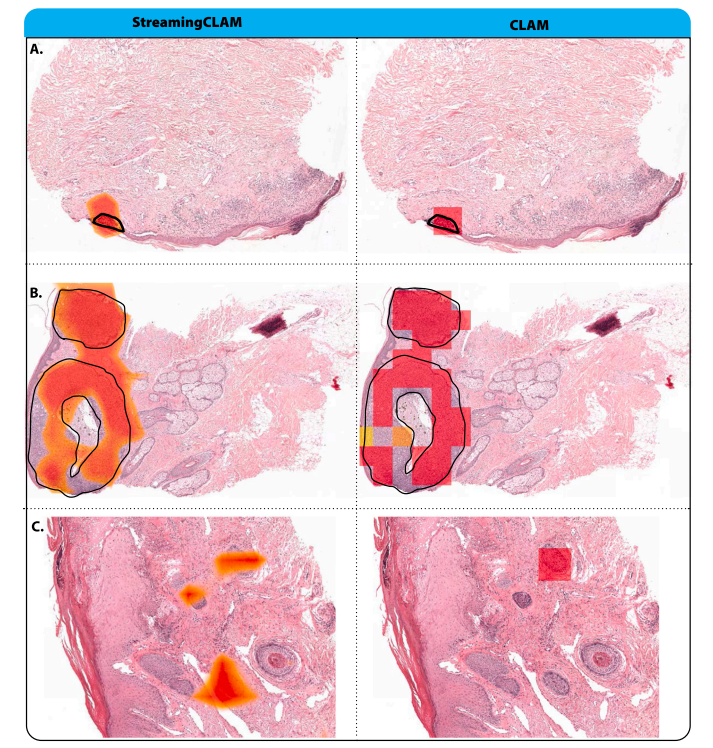
Fig. 5. Attention maps for both StreamingCLAM and CLAM models. (A) Both models show high attention values in a confined region corresponding to the tumor area (indicatedby the black line). Inflammated areas and crusts, often present near tumor sites, receive low attention values. (B) A larger tumor region (highlighted by the black line) whereboth models exhibit high attention values. Adnex structures and color artifacts are disregarded by the models, as evidenced by their low attention values. (C) Illustration of afalse positive: both models concentrate on hair follicles. It is probable that the models identified these slides as positive due to the resemblance of these hair follicles to basal cellcarcinoma (BCC) features.
图 5. StreamingCLAM 和 CLAM 模型的注意力图。(A) 两个模型在与肿瘤区域(黑线标示)相对应的限定区域内显示出较高的注意力值。炎症区域和痂皮,通常位于肿瘤部位附近,表现出低注意力值。(B) 一个更大的肿瘤区域(黑线标示),两个模型均在此区域显示出高注意力值。附属结构和颜色伪影被模型忽略,表现为低注意力值。(C) 错误阳性示例:两个模型都集中在毛囊上。模型可能将这些切片识别为阳性,因为这些毛囊的特征与基底细胞癌 (BCC) 的特征相似。
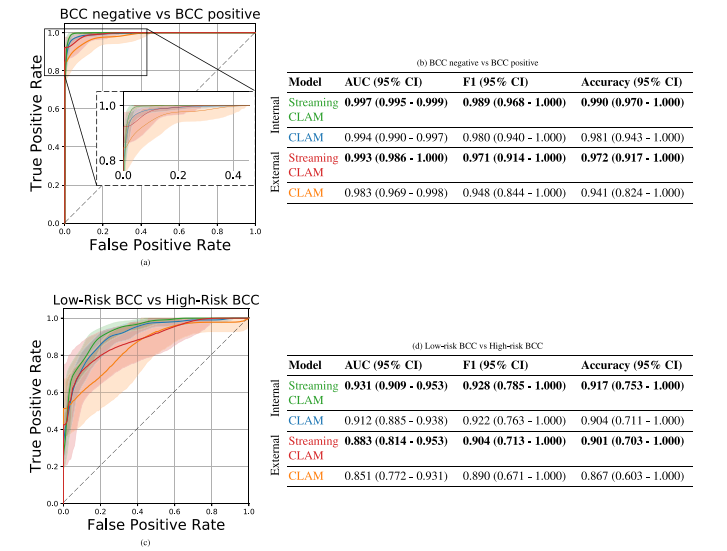
Fig. 6. Figure a. and Table b. show the ROC curves and metrics for discriminating between non-BCC and BCC lesions, while Figure c. and Table d. show the ROC curves andmetrics for stratifying BCC risk into low-risk and high-risk categories. The ROC curves are generated using bootstrapped samples, with the shaded areas representing 95% confidenceintervals. The figures display the ROC curves of two models (CLAM and StreamingCLAM) evaluated on an internal and external dataset, represented by the corresponding colorsin the tables. The tables show the mean AUC, mean F1, and mean accuracy for both tasks with 95% CI.
图 6. 图 a 和表 b 显示了用于区分非 BCC 和 BCC 病灶的 ROC 曲线和指标,而图 c 和表 d 显示了用于将 BCC 风险分为低风险和高风险类别的 ROC 曲线和指标。ROC 曲线基于自助法样本生成,阴影区域表示 95% 置信区间。图中展示了在内部和外部数据集上评估的两个模型(CLAM 和 StreamingCLAM)的 ROC 曲线,不同颜色对应于表中的数据集。表格显示了两个任务的平均 AUC、平均 F1 和平均准确率,以及 95% 置信区间。
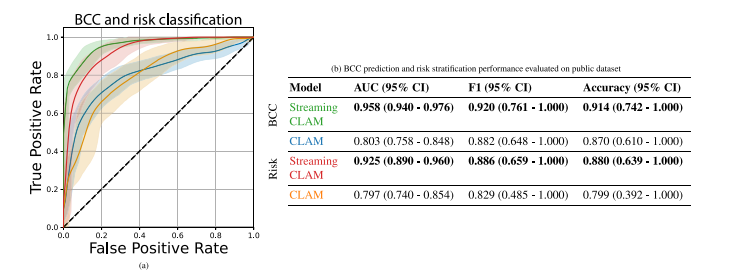
Fig. 7. All evaluations performed on a public dataset. Figure a. and Table b. display the ROC curves and performance metrics for two tasks: (1) discriminating between non-BCCand BCC lesions and (2) stratifying BCC risk into low-risk and high-risk categories. Both the Streaming CLAM and CLAM models’ results are included for each task. The ROCcurves, generated using bootstrapped samples, are shown with shaded areas indicating the 95% confidence intervals. Different colors in the figures correspond to the two models’results, which are elaborated in the tables. Table b. provides the mean AUC, mean F1, and mean accuracy for both detection and risk classification tasks with their 95% CI.
图 7. 在公共数据集上进行的所有评估。图 a 和表 b 显示了两个任务的 ROC 曲线和性能指标:(1)区分非 BCC 和 BCC 病灶,(2)将 BCC 风险分为低风险和高风险类别。每个任务均包含 Streaming CLAM 和 CLAM 模型的结果。ROC 曲线基于自助法样本生成,阴影区域表示 95% 置信区间。图中不同颜色表示两个模型的结果,具体数据在表中详细列出。表 b 提供了检测和风险分类任务的平均 AUC、平均 F1 和平均准确率及其 95% 置信区间。
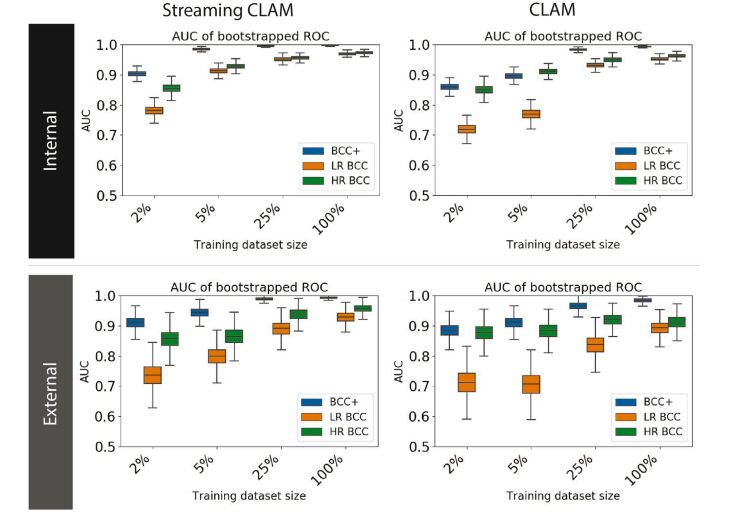
Fig. 8. Each boxplot displays the distribution of AUC values from bootstrapped samples of two models (StreamingCLAM and CLAM) on two datasets (Internal and External). Thefour groups in each boxplot correspond to the amount of data used to train the models (2%, 5%, 25%, and 100%). The discrimination tasks shown are non-BCC vs BCC (BCC+),and the stratification of BCC risk into low-risk (LR BCC) and high-risk (HR BCC) categories. The AUC values are shown for each task and dataset combination. The horizontalline within each box represents the median, the box represents the interquartile range (IQR), and the whiskers extend to the most extreme data points within 1.5 times the IQR.Outliers are not shown.
图 8. 每个箱线图展示了两个模型(StreamingCLAM 和 CLAM)在两个数据集(内部和外部)上的 AUC 值分布,这些值来自自助法样本。每个箱线图中的四组数据分别对应用于训练模型的数据量(2%、5%、25% 和 100%)。显示的区分任务包括非 BCC 与 BCC(BCC+)的区分,以及将 BCC 风险分为低风险(LR BCC)和高风险(HR BCC)类别的分层。AUC 值展示了每个任务和数据集组合的结果。箱线图中的水平线表示中位数,箱体表示四分位距 (IQR),须线延伸到 1.5 倍 IQR 范围内的最极端数据点。离群值未显示。
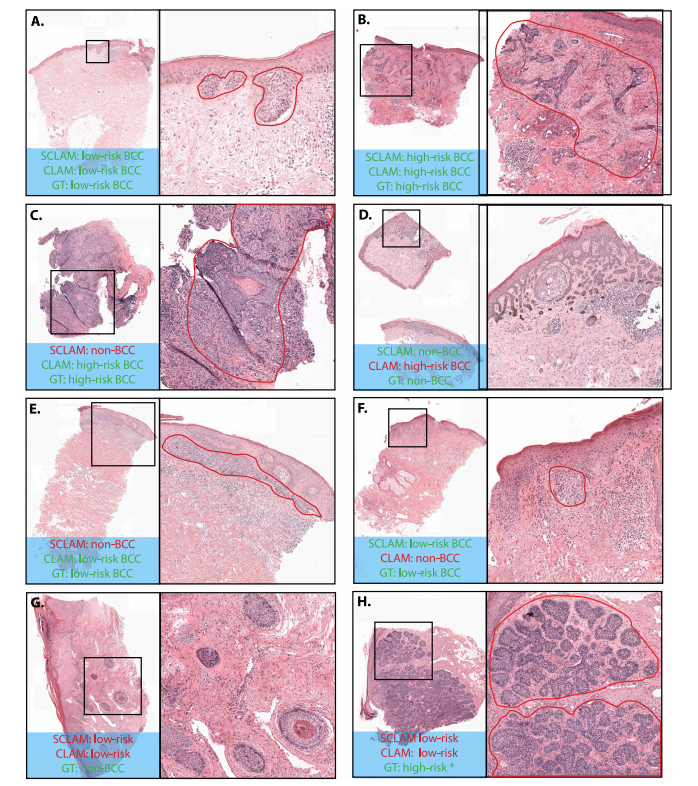
Fig. 9. Whole Slide Images of BCC lesions with close-up Regions of Interest (ROIs) and model predictions. In the ROIs, the tumor area is outlined in red. The top row (A–B)shows cases where StreamingCLAM (SCLAM) and CLAM agree with the ground truth (GT). The second (C–D) and third (E–F) rows show cases where either StreamingCLAM orCLAM makes an incorrect prediction in either BCC detection or risk stratification. The last row (G–H) shows a false positive case where both models predict low-risk BCC insteadof non-BCC, and another case where both models predict low-risk BCC while the ground truth is high-risk BCC. After inspection by pathologists LH and AA, it was determinedthat this case had been mislabeled as high-risk BCC and should have been labeled as low-risk BCC.
图 9. 基底细胞癌 (BCC) 病灶的全切片图像及感兴趣区域 (ROIs) 的特写和模型预测。在 ROIs 中,肿瘤区域用红色勾勒。第一行 (A–B) 显示了 StreamingCLAM (SCLAM) 和 CLAM 与真实值 (GT) 一致的案例。第二行 (C–D) 和第三行 (E–F) 显示了 StreamingCLAM 或 CLAM 在 BCC 检测或风险分层中出现错误预测的案例。最后一行 (G–H) 显示了一个假阳性案例,其中两个模型都预测为低风险 BCC 而非非 BCC,以及另一个两个模型都预测为低风险 BCC 而真实值为高风险 BCC 的案例。* 在病理学家 LH 和 AA 的检查下,确认该案例被错误标记为高风险 BCC,实际应标记为低风险 BCC。
相关文章:

利用弱监督学习在全切片病理图像中检测和分型基底细胞癌|文献速递-基于生成模型的数据增强与疾病监测应用
Title 题目 Detection and subtyping of basal cell carcinoma in whole-slide histopathology using weakly-supervised learning 利用弱监督学习在全切片病理图像中检测和分型基底细胞癌 01 文献速递介绍 基底细胞癌 (BCC) 的发病率正在给病理诊断带来压力。BCC 的发病率…...

leetcode刷题笔记——15.三数之和
一、问题描述 给定一个整数数组 nums,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]],使得: i ! j、i ! k 且 j ! k nums[i] nums[j] nums[k] 0 需要返回所有和为 0 的三元组,且这些三元组不能重复。 输入输出 输入: 整…...

NLTK无法下载?
以下内容仅为当前认识,可能有不足之处,欢迎讨论! 文章目录 nltk无法下载怎么办?什么是NLTK?为什么要用NLTK?如何下载? nltk无法下载怎么办? 什么是NLTK? NLTK是学习自然…...
)
采用非递归快排实现找出数组中的前k个高频元素(python)
前k个高频元素 题目描述解题思路代码实现 题目描述 给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。 输入: nums [1,1,1,2,2,3], k 2 输出: [1,2] 解题思路 (1)先对给定的列表进行…...

Java题集练习4
Java题集练习4 1 异常有什么用? 用来找到代码中产生的错误 防止运行出错2 异常在java中以什么形式存在? 异常在java中以类的形式存在,分为运行时异常和编译期异常,他们都在类Exception中3 异常是否可以自定义?如何自…...

sql进阶篇
1.更新记录 AC: update examination_info set tag replace(tag, "PYTHON", "Python") where tag "PYTHON";2.删除记录 AC: DELETE FROM exam_record WHERE timestampdiff(minute, start_time, submit_time) < 5AND…...

代码工艺:SQL 优化的细节
1. 巧用 limit 当出现深分页的时候,例如: select id, name, status, detail from product limit 100000, 30; 那么MySQL的执行方式为:一共需要查100030条数据,然后丢弃前面的100000条,只返回后面的30条数据…...

天池蚂蚁AFAC大模型挑战赛-冠军方案(含代码)
天池-蚂蚁AFAC大模型挑战赛-冠军方案 前言 ❝ 作者 彭欣怡 华东师大; 马千里 虾皮; 戎妍 港科广 说在前面 在当今信息技术迅猛发展的背景下,大模型技术已经成为推动人工智能领域进步的重要力量。 前段时间备受瞩目的AFAC赛题聚焦于金融对话…...

[QUIC] Packets 和 Frames 概述
Packets 和 Frames 概述 受保护的数据包 (Protected Packets) 基于不同的包类型, QUIC 使用不同等级的保护机制. Version Negotoation 包不受保护. Retry 包使用 AEAD 进行保护。 Initial 包使用 AEAD 进行保护, 但是使用的 Key 是由一个网络可见的值计算出来的。 因此 Ini…...

QT编辑框带行号
很可惜,qt的几个编辑框并没有相关功能。所以我们要自己实现一个。 先讲讲原理: QPlainTextEdit继承自QAbstractScrollArea,编辑发生在其viewport()的边距内。我们可以通过将视口的左边缘设置一个空白区域,…...

Kafka认证时Successfully logged in真的认证成功了?
背景 某个应用需要配置 Kafka 集群信息,且需要在验证集群是否可达。基本实现思路是创建一个生产者对象,然后发送一条测试数据,调用 Producer 的 send 方法发送消息后,再调用 get() 方法,即同步发送消息,测…...

软考信息系统管理师,系统集成项目管理工程师,考哪一个合适?
根据2024年的考试安排,高级项目管理师和系统集成工程师考试改为每年一次。 2024年上半年考高级项目管理师,下半年考系统集成项目管理工程师。 根据这个调整,建议先报名5月份的高级项目管理师考试。如果通过了,大家都高兴&#x…...
)
AI学习指南自然语言处理篇-位置编码(Positional Encoding)
AI学习指南自然语言处理篇-位置编码(Positional Encoding) 目录 引言位置编码的作用位置编码的原理绝对位置编码相对位置编码位置编码在Transformer中的应用位置编码的意义总结 引言 在自然语言处理中,文本数据通常以序列的形式存在。然而…...

macOS 15 Sequoia dmg格式转用于虚拟机的iso格式教程
想要把dmg格式转成iso格式,然后能在虚拟机上用,最起码新版的macOS镜像是不能用UltraISO,dmg2iso这种软件了,你直接转放到VMware里绝对读不出来,办法就是,在Mac系统中转换为cdr,然后再转成iso&am…...

【01初识】-初识 RabbitMQ
目录 学习背景1- 初识 MQ1-1 同步调用什么是同步调用?小结:同步调用优缺点 1-2 异步调用什么是异步调用?小结:异步调用的优缺点,什么时候使用异步调用? 1-3 MQ 技术选型 学习背景 异步通讯的特点ÿ…...

CTF-RE 从0到N:汇编层函数调用
windows 在 Windows 平台上的汇编语言中,调用函数的方式通常遵循特定的调用约定(Calling Convention)。最常见的调用约定包括: cdecl: C 默认调用约定,调用者清理堆栈。stdcall: Windows API 默认调用约定࿰…...

雷池社区版compose配置文件解析-mgt
在现代网络安全中,选择合适的 Web 应用防火墙至关重要。雷池(SafeLine)社区版免费切好用。为网站提供全面的保护,帮助网站抵御各种网络攻击。 compose.yml 文件是 Docker Compose 的核心文件,用于定义和管理多个 Dock…...
无人机避障——4D毫米波雷达Octomap从点云建立三维栅格地图
Octomap安装 sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-ros sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-msgs sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-server sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-octomap-rviz-plugins # map_server安装 sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-…...

Python(数据结构2)
常见数据结构 队列 队列(Queue),它是一种运算受限的线性表,先进先出(FIFO First In First Out) Python标准库中的queue模块提供了多种队列实现,包括普通队列、双端队列、优先队列等。 1 普通队列 queue.Queue 是 Python 标准库 queue 模块中的一个类…...
深入解析HTTP与HTTPS的区别及实现原理
文章目录 引言HTTP协议基础HTTP响应 HTTPS协议SSL/TLS协议 总结参考资料 引言 HTTP(HyperText Transfer Protocol)超文本传输协议是用于从Web服务器传输超文本到本地浏览器的主要协议。随着网络安全意识的提高,HTTPS(HTTP Secure…...

TDengine 快速体验(Docker 镜像方式)
简介 TDengine 可以通过安装包、Docker 镜像 及云服务快速体验 TDengine 的功能,本节首先介绍如何通过 Docker 快速体验 TDengine,然后介绍如何在 Docker 环境下体验 TDengine 的写入和查询功能。如果你不熟悉 Docker,请使用 安装包的方式快…...
Debian系统简介
目录 Debian系统介绍 Debian版本介绍 Debian软件源介绍 软件包管理工具dpkg dpkg核心指令详解 安装软件包 卸载软件包 查询软件包状态 验证软件包完整性 手动处理依赖关系 dpkg vs apt Debian系统介绍 Debian 和 Ubuntu 都是基于 Debian内核 的 Linux 发行版ÿ…...
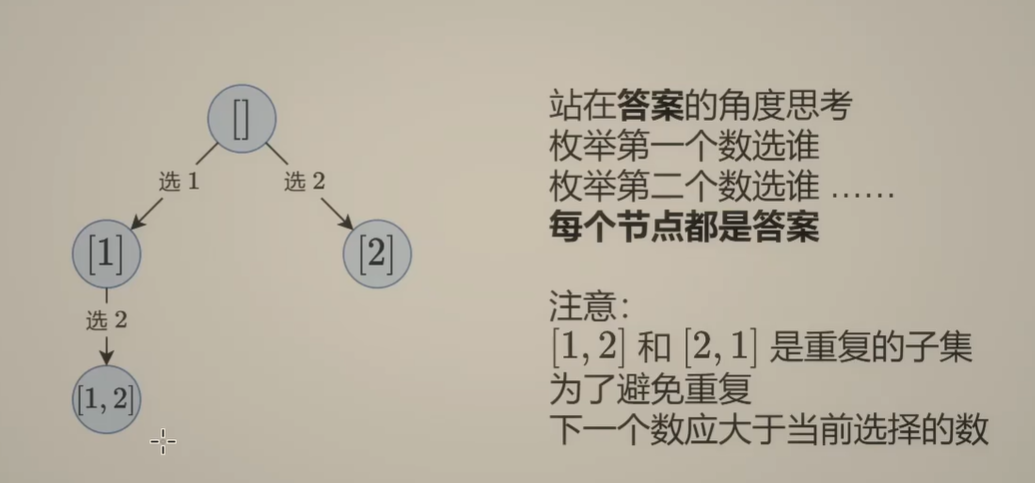
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集 78.子集 78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路: 笔者写过很多次这道题了,不想写题解了,大家看灵神讲解吧 回溯算法套路①子集型回溯【基础算法精讲 14】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 完…...

Linux简单的操作
ls ls 查看当前目录 ll 查看详细内容 ls -a 查看所有的内容 ls --help 查看方法文档 pwd pwd 查看当前路径 cd cd 转路径 cd .. 转上一级路径 cd 名 转换路径 …...
 自用)
css3笔记 (1) 自用
outline: none 用于移除元素获得焦点时默认的轮廓线 broder:0 用于移除边框 font-size:0 用于设置字体不显示 list-style: none 消除<li> 标签默认样式 margin: xx auto 版心居中 width:100% 通栏 vertical-align 作用于行内元素 / 表格单元格ÿ…...
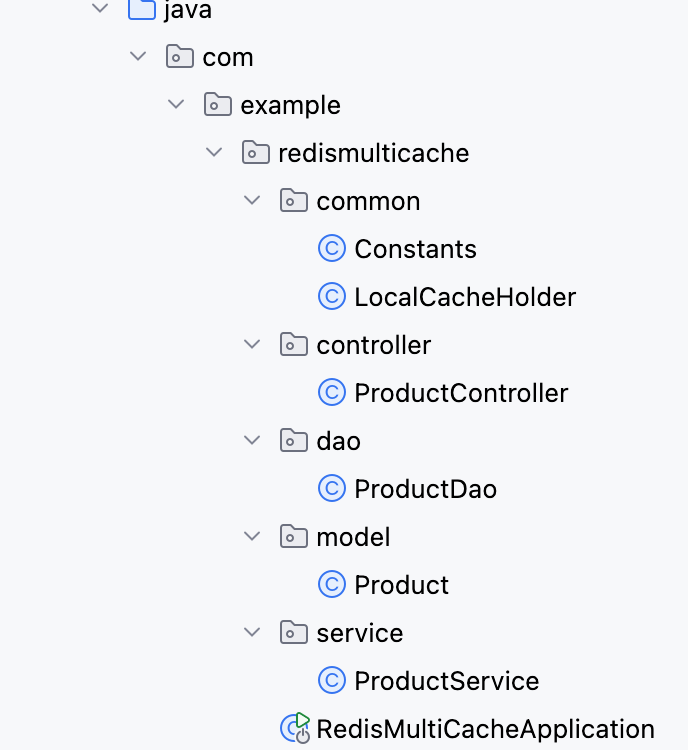
【Redis】笔记|第8节|大厂高并发缓存架构实战与优化
缓存架构 代码结构 代码详情 功能点: 多级缓存,先查本地缓存,再查Redis,最后才查数据库热点数据重建逻辑使用分布式锁,二次查询更新缓存采用读写锁提升性能采用Redis的发布订阅机制通知所有实例更新本地缓存适用读多…...

CRMEB 中 PHP 短信扩展开发:涵盖一号通、阿里云、腾讯云、创蓝
目前已有一号通短信、阿里云短信、腾讯云短信扩展 扩展入口文件 文件目录 crmeb\services\sms\Sms.php 默认驱动类型为:一号通 namespace crmeb\services\sms;use crmeb\basic\BaseManager; use crmeb\services\AccessTokenServeService; use crmeb\services\sms\…...
c++第七天 继承与派生2
这一篇文章主要内容是 派生类构造函数与析构函数 在派生类中重写基类成员 以及多继承 第一部分:派生类构造函数与析构函数 当创建一个派生类对象时,基类成员是如何初始化的? 1.当派生类对象创建的时候,基类成员的初始化顺序 …...
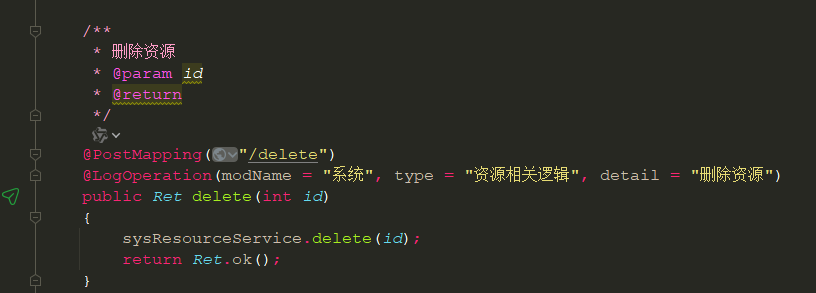
springboot 日志类切面,接口成功记录日志,失败不记录
springboot 日志类切面,接口成功记录日志,失败不记录 自定义一个注解方法 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target;/***…...

vue3 daterange正则踩坑
<el-form-item label"空置时间" prop"vacantTime"> <el-date-picker v-model"form.vacantTime" type"daterange" start-placeholder"开始日期" end-placeholder"结束日期" clearable :editable"fal…...
